
Virtual Domain, Skill & Maturity
Eduranet Education System has discovered that every human brain functions within a particular domain (a specific area). This domain is referred to here as ‘Virtual Domain’. This virtual domain is the combination of Cognitive, Affective and Psychomotor domains and it acts like a medium for human communication within the limited territory (range). The cognitive domain is the domain within which the human brain's intellectual powers are tested. The affective domain is the domain within which emotions, feelings or values are influenced by others. That is, it is a process by which another person's, group's or society's ideas, beliefs, customs, philosophies, attitudes and so on are gradually accepted and internalised. The psychomotor domain comprises of all behaviours: speaking (the way one speaks), writing, eating, jumping, throwing, driving a car, watching TV etc., In short, the psychomotor domain represents the most complex forms of nonverbal communication. The functions of a human brain are influenced by these three aspects which form the virtual domain.
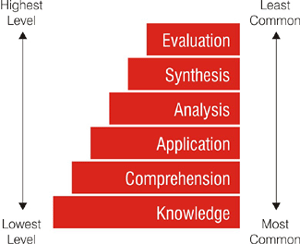
According to Bloom’s Taxonomy, one method of categorizing educational objectives is delineating six levels of cognitive complexity, ranging from the knowledge level (simplest) to the evaluation level (most complex). See figure below.
The level of an objective refers to the cognitive, mental, or thought complexity called for the objective. For Example, the objective “The student will list from memory the names of at least three of the last four Indian Presidents” is a relatively straight- forward cognitive task. It involves only recall of the information. Such an objective would be considered lower level. In contrast, an objective such as “Give an eyewitness account of an event, separate fact from opinion with at least 75% accuracy” is a relatively complex cognitive task.
It requires the ability to analyse an eyewitness account and to apply some criteria in determining whether statements are observable and objective or subjective and based on inference. Such an objective would be considered higher level.
According to Eduranet Education System, knowledge is the common objective at all these six levels of cognitive complexity. At every level, the end result (i.e., comprehension, application etc.,) is the result of multiplication of knowledge with relevant variables as shown in the table below.
| # | Education Objectives |
|---|---|
| 1 | Knowledge x Understanding = Comprehension |
| 2 | Knowledge x Implementation = Application |
| 3 | Knowledge x Fact Finding = Analysis |
| 4 | Knowledge x Creativity = Synthesis |
| 5 | Knowledge x Judgement = Evaluation |
Table: Taxonomy of Education objectives: Cognitive domain.
Note: Understanding, Implementation, Fact-finding, Creativity and Judgement are the variables.
Eduranet strongly believes that education is the culmination of acquisition of total knowledge through different levels, i.e., comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation over a span of time.
Eduranet concludes that there is a strong interrelation between Knowledge(K), Time(T) and Education(E). We have discussed this concept in detail in 'Learning Management'.
Gaining knowledge, receiving and responding to specific queries or suggestions and exhibiting behaviours like reflex & skilled movements, perceptive & physical abilities are all part of the learning process.
This process finds expression in the arena called the Virtual Domain (as explained earlier). The human brain has an innate sense to follow this learning process spontaneously. And Eduranet terms this sense as the 'Learning Sense'. In majority cases, human intellectual development depends on the maturity level of the learning sense.
The key functions of a human brain's learning sense:

Managing & storing the knowledge in the ‘Data Bank’ is another vital part of the Learning Sense. The Data Bank is the combination of different blocks in the human brain, which stores the knowledge gained by experience, observation, learning etc. Memory is an act which creates links between alerts and data stores and which helps find appropriate information from the bulk data bank.
For example: In a class room, a student Rajesh listens to the mathematics teacher with rapt attention. Here, two of the alerts, viz., sight & hearing initiate his thinking and understanding actions in his brain. After this, his memory starts to store the gained knowledge (by thinking and understanding what the teacher says) in his brain’s data bank. When the teacher asks relevant questions to test the concentration levels of the student, the latter’s brain activates the recall action and supports memory to find out the right knowledge block, that supplies the student the correct answers. This is a common and continuous process in every individual. The figure below explains the process:
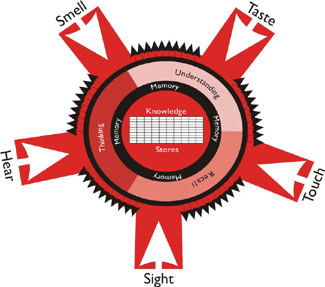
Learning Sense
2. Modes to activate Learning Sense:
“Learning is like breathing we do it all the time”.
We learn throughout our lives. Some of this learning is deliberate and planned, and some simply happens as a result of our experience.
The following are the three modes to activate learning sense:
(i) Learning by Experience:
Trial and error or real time problem is used to acquire experience in problem-solving. An expert uses experience to explain how a problem is solved.
Although most of us recognize and value the learning we gain through our formal education and training, we do not always place equal value to our informal learning. By far the greatest part of our learning is achieved outside formal education and training. We learn immensely through our everyday experiences by watching others, asking questions, solving problems and experiencing success or failure.
Learning from our experience involves more than just gaining the experience itself. It also involves thinking through the experience to interpret and extract its meaning, in order to improve our understanding, knowledge and skills.
“Tell me, I forget; teach me I remember; involve, I learn”, so said Benjamin Franklin.
(ii) Learning by Example:
Learning will be much more effective when the teacher explains different subjects with related examples. Especially, constructed examples or scenarios when used, develop the concept(s) the student is expected to learn more convincingly.
"A good example has twice the value of good advice"-so goes the saying”.
(iii) Learning by Discovery:
'Discovery' is gaining first time knowledge of a thing that already exists.. This is an undirected approach, where the learners explore a problem area with no advance knowledge of what their object is.
As one intellectual said, “Discovery consists of seeing what everybody has seen and thinking what nobody has thought”.
Eduranet Education System has developed useful material based on these three major modes to activate the learning sense and the same material will be sent to the members of the system periodically.
3. Skills to sharpen
Eduranet will assess the members' knowledge and performance in the following skills and guide them in improving them. This will in turn help to excel in their studies/work.
- Basic Skills :
- Active Listening - Listening, remembering and understanding what other people are saying and asking appropriate questions.
- Concentrating - The ability to focus and not be distracted while performing a task over a period of time.
- Reading Comprehension - Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
- Self-Assessment - Evaluating your own ability for learning or doing something.
- Speaking - Talking to others to effectively convey information.
- Using Logic and Analysis - Using reason and methods of proof to identify the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches.
- Using Multiple Learning Strategies - Approaching learning or teaching from a variety of methods while learning or teaching new things.
- Hearing and Vision Skills (Distinguishing Sound, Sight Perception)
- Communication Skills (Expressing and Understanding Verbal and Written Ideas)
- Reasoning Skills (Ideas, Memory, Problem Solving)
- Management Skills (Managing available resources and system application skills)
- Movement Skills (Strength, Endurance, Balance, Reaction)
- Interpersonal Skills (Teaching, Persuasion, Helping Others, Awareness)
- Numerical Skills (Mathematical Calculations and Reasoning)
- Judgement Skills (Apt perception and decision-making)
- Technical Skills (Using Equipment, Programming, Troubleshooting)
Eduranet Education System has developed relevant material on nurturing these skills and the same will be dispatched to our members from time to time.
4. How to attain maturity?
Maturity of mind helps students think positively and take correct decisions at the correct time. Mental growth or maturity varies from individual to individual. Some people develop greater mental maturity and rationality earlier in their lives when compared to others. At times, the same individual may exhibit varying degrees of maturity on different occasions.
What is maturity? Maturity need not necessarily come with age. In fact, it comes with awareness and understanding. To be mature does not necessarily mean just a fully-grown up individual. It is a combination of many things that includes age, awareness, intelligence, decision-making ability and more.
To be mature means:
- to be realistic, i.e., making realistic evaluation of things.
- to be responsible to self and others.
- to be ready to be guided by reason rather than emotion.
- to be assertive without being aggressive or adamant.
- to be flexible or open-minded without being rigid or temperamental.
- to be inquisitive (i.e., eager to learn new things).
- And to be able to act instantly, according to the situation without succumbing to preconceived notions.
Eduranet has done extensive study on the maturity levels of learners and the factors that influence them. Eduranet has prepared useful material on the ways to attain maturity, which helps students achieve their set targets without stress or strain. This exclusive material will be made available only to the members of Eduranet Education System.
NOW, take a 'mature' decision!
Learning Sense course in the distance-learning mode has been designed exclusively for the benefit of teachers, who are committed to bringing about beneficial changes in their teaching techniques.